
Intro to Cannabis

The Cannabis Plant
 Cannabis is a flowering plant that has been used for medicinal purposes for millenniums. The plant can be used for fiber to make cloth and rope, as food and medicine, and for its psychoactive properties for religious and recreational use.
Cannabis is a flowering plant that has been used for medicinal purposes for millenniums. The plant can be used for fiber to make cloth and rope, as food and medicine, and for its psychoactive properties for religious and recreational use.
The female plants grow the flowers (buds) that have small translucent or white looking crystals. These crystals are called trichomes. Trichomes were developed to protect the plant against predators. They secrete wonderfully fragrant oils (Terpenes) and contain an array of therapeutic cannabinoids such as the commonly known THC and CBD.
Cannabinoids and Medicinal Effects
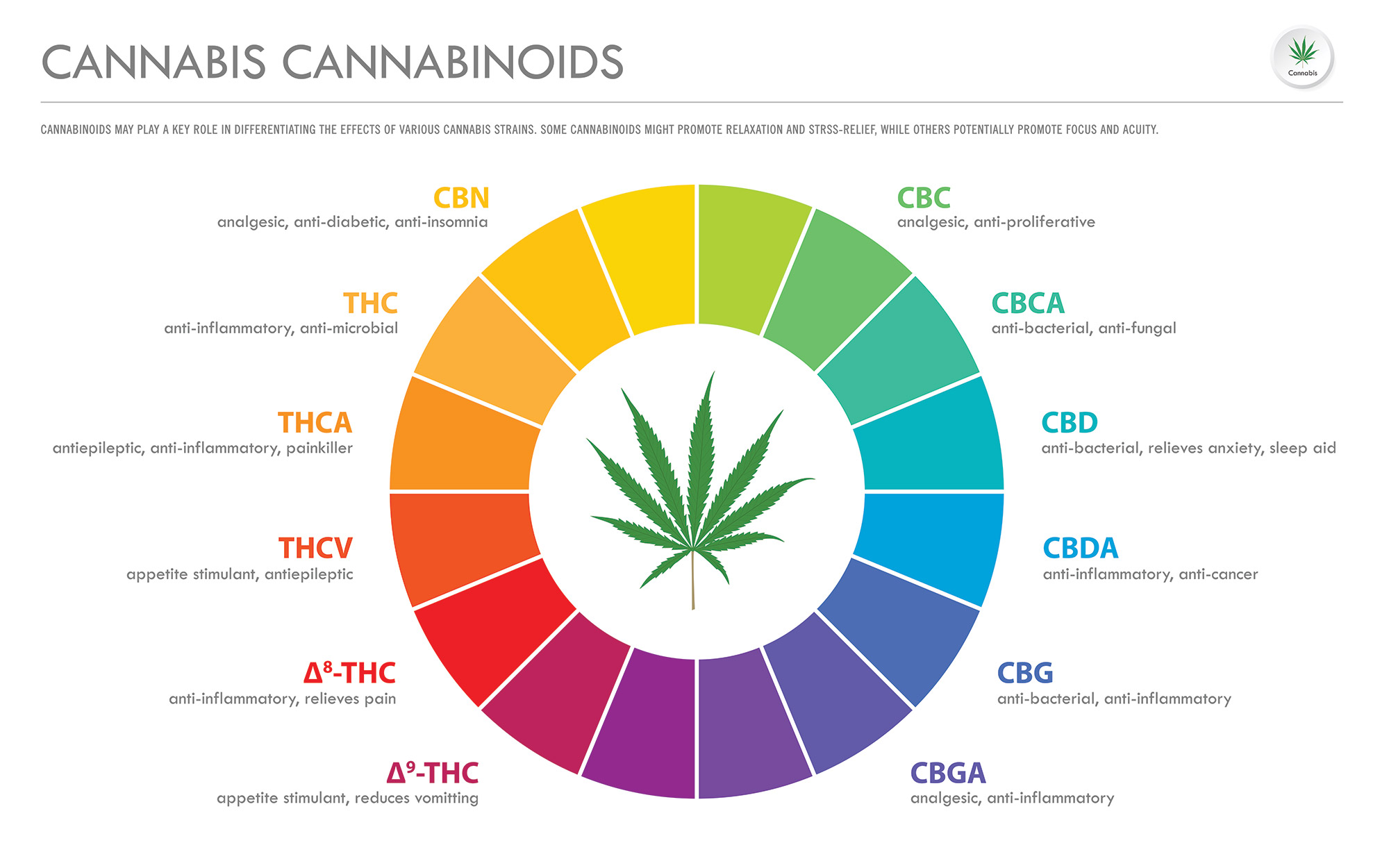
Cannabis’ effect on the human body is in large part due to its collection of Cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds secreted by the plant’s trichomes that offer a wide array of therapeutic benefits. Research has found that the cannabis plant produces between 80 and 100 cannabinoids and about 300 non-cannabinoid chemicals. The two most common cannabinoids are delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Cannabinoids bind to receptor sites in the human brain and body called the Endocannabinoid System.
Endocannabinoid System

Endocannabinoid System (ECS) are the special molecules naturally produced in the human body that relate to the immune and nervous systems. ECS regulates the ‘homeostatic’ balance in our body’s systems. This homeostatic balance is necessary to achieve total body wellness. Imbalances in any or all the body’s systems can lead to disease. Our body attempts to achieve balance by maintaining an ECS tone. The human body produces its own endocannabinoids (Anandamide and 2AG) to help maintain its ECS tone. Organically grown “full spectrum” cultivars provide phyto-cannabinoids that have shown promise when used to assist our own ECS homeostatic balance. Cannabinoids fit perfectly into specialized receptors found throughout our nervous and immune systems, serving to enhance, or improve upon, the body’s own ability to maintain homeostasis (balance) and health.
The science behind cannabinoids as medicine is becoming well documented. The two most studied cannabinoids, THC and CBD, have been shown to help patients suffering from pain, nausea, sleep, stress relief, anxiety, inflammation, and epilepsy. Since cannabis contains 80-100 different cannabinoids, more research will become available on how cannabinoids can be used to treat a wider range of ailments.
Like traditional modern medicine, cannabis can be precisely dosed. Cannabis is now available in pills, gel caps, tablets etc., that contain exact amounts of the active ingredients needed or desired.
Cannabis Strain Types
 By definition, a strain is a genetic variant of a species. Plant strains are variations of the same species that share a common ancestor. There are three main biological subspecies of cannabis: Cannabis Sativa, Cannabis Indica, and Cannabis Ruderalis. Today’s modern cannabis strains are classified as either Cannabis Sativa or Cannabis Indica. However, hybrid genetics have been created through genetic crossbreeding that combine both indica and sativa varieties. The goal is to develop plant profiles using the best attributes of both parent strains.
By definition, a strain is a genetic variant of a species. Plant strains are variations of the same species that share a common ancestor. There are three main biological subspecies of cannabis: Cannabis Sativa, Cannabis Indica, and Cannabis Ruderalis. Today’s modern cannabis strains are classified as either Cannabis Sativa or Cannabis Indica. However, hybrid genetics have been created through genetic crossbreeding that combine both indica and sativa varieties. The goal is to develop plant profiles using the best attributes of both parent strains.
Sativa and Indica strains tend to have very different effects on the consumer. Breeding different strains allows the cultivator to create specific flavor profiles, plant yields, potency, growing time, size, and cannabinoid profiles.
Some of the major differences between strains are the flavor profiles. Cannabis gets its flavor and aroma from oils called terpenes. Terpenes not only make our cannabis taste and smell amazing, but they’re responsible for the unique experience that each strain gives us. This is because terpenes change the way THC affects. Indicas and Sativas have vastly different terpene profiles.
Indica vs. Sativa vs. Hybrids
The efficacy expectations of Sativas vs Indicas have become too general. It is the combination of a strain’s cannabinoids and terpenes that greatly influences its effects. That is why it’s important to understand the individual strains profile to understand its benefits for you.
 Indicas are from the mountainous regions of Asia and the Middle East. Indica plants tend to be short and stocky, and their leaves are broad and chunky. Indicas traditionally promote relaxation and general calming. Often, Indicas are thought to be very beneficial for pain relief, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Strong Indicas might not be the best option for morning-use and wanting to stay productive.
Indicas are from the mountainous regions of Asia and the Middle East. Indica plants tend to be short and stocky, and their leaves are broad and chunky. Indicas traditionally promote relaxation and general calming. Often, Indicas are thought to be very beneficial for pain relief, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Strong Indicas might not be the best option for morning-use and wanting to stay productive.
 Sativas are from more equatorial regions around the world. Sativa plants are tall and lanky with thin and pointy leaves. Pure sativa will likely have a powerful uplifting/energizing effect. Sativas can promote focus and productivity – making them preferable for day-time use. However, strong sativas can cause a person’s mind to race and cause users to feel anxious or paranoid.
Sativas are from more equatorial regions around the world. Sativa plants are tall and lanky with thin and pointy leaves. Pure sativa will likely have a powerful uplifting/energizing effect. Sativas can promote focus and productivity – making them preferable for day-time use. However, strong sativas can cause a person’s mind to race and cause users to feel anxious or paranoid.
 Hybrids are bred with a mix of sativa and indica encompassing the pros and cons of each species. Hybrid strains bred with more indica are called indica-dominant. Conversely, sativa-dominant strains have mostly sativa traits, but are tempered by the indica influence.
Hybrids are bred with a mix of sativa and indica encompassing the pros and cons of each species. Hybrid strains bred with more indica are called indica-dominant. Conversely, sativa-dominant strains have mostly sativa traits, but are tempered by the indica influence.
Cannabis Effects
 Suffice it to say, Cannabis affects everyone differently. Different strains and methods of consumption command different effects. More experienced users tend to have a different experience than new users.
Suffice it to say, Cannabis affects everyone differently. Different strains and methods of consumption command different effects. More experienced users tend to have a different experience than new users.
Since results can vary, it is hard to say for sure how it will affect you. Some people don’t feel anything the first time they try cannabis. Most often, the experience is one of relaxation. Some people tend to be more outgoing and social. Conversely, others find cannabis makes them tired, and anxious.
Therefore, it is recommended to consume cannabis slowly with a low dosage and see how it affects you. Keeping track of your dosing, strains, type of product and the feelings you experienced will help you better understand how cannabis can best work for you.
Forms of Consumption
There are many ways to consume cannabis. Long gone are the days when cannabis was only smoked.
The most common forms of cannabis consumption:

Inhalation: (Joints, Pipes, and Vaporizers)
Inhalation delivers the fastest effects to the consumer. When cannabis is inhaled, the cannabinoids enter the body through the lungs where they are passed along directly into the consumer’s blood stream. The effect is almost instantaneous.

Oral: (Edibles, Tinctures, Capsules and Oils)
Cannabis can also be ingested orally. The cannabinoids and terpenes are extracted from the flower as oil and ingested as-is or combined with another medium. The effects are slower but stronger and last longer than with inhalation. When consumed orally, the effects are usually felt within thirty minutes to an hour, with peak effects around the two-hour mark. The effects can last up to six hours as cannabinoids undergo a chemical transformation making them stronger during digestion.

Sublingual: (Dissolvable strips, Sublingual sprays, Lozenges and Tinctures)
The extracted cannabis oil when combined with another medium can also enter the blood stream when placed under the tongue or held in the mouth, as the mouth contains many blood vessels to absorb the cannabinoids.

Topicals: (Lotions, Salves, Transdermal Patches, Oils)
Cannabis can also be applied topically to the skin. The cannabinoids penetrate the skin working to reduce pain and inflammation. This method is a popular choice with older consumers because it works well on localized pain (arthritis) and is non-psychoactive. It is reported that topicals work within minutes when applied to local areas with effects lasting one to two hours. Topicals do not allow a significant number of cannabinoids to reach the brain thus it is unlikely to cause intoxication.
Terpenes

Female cannabis plants grow flowers (buds) that have small translucent or white looking crystals. These crystals are called trichomes. Trichomes were developed to protect the plant against predators. They secrete wonderfully fragrant oils (Terpenes) and contain an array of therapeutic cannabinoids such as THC and CBD.
Not only do cannabis Terpenes determine the scent of its plant (strains), but they also provide therapeutic benefits like their cannabinoid partners, THC and CBD. Terpenes interact with the body’s cells and messenger systems to produce different physiological effects. Depending on which receptors they react with, different terpenes may help to induce sleep or relax muscles while others reduce stress and elevate mood or reduce inflammation and increase energy.
When terpenes and cannabinoids work together, they increase the level of each other’s effectiveness. This is called the Entourage Effect. Terpenes modify how much of each cannabinoid is absorbed thus the presence of certain terpenes can increase or decrease the amount of the psychoactive cannabinoid THC is absorbed, effectively controlling the potency.
There are more than 200 known cannabis terpenes. Here are some of the more common ones found in cannabis.
Limonene
Limonene is known for its mouthwatering smell of citrus. It can also convert into the lemon, orange, grapefruit, lime, mint, rosemary, or juniper aroma.
 Limonene is found to produce the following effects:
Limonene is found to produce the following effects:
- Stress relief
- Elevated mood
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anti-bacterial
- Anti-fungal
- Aids digestion
- Acid reflux relief
Linalool
Linalool produces the floral, spicy, and woody aromas. Also found in some citrus, birch, rosewood, laurels and coriander, linalool is behind the beautiful calming scent of lavender. Linalool is also thought to be one of the oldest known sedatives, or sleep aids, in the world.
 Linalool is found to produce the following effects:
Linalool is found to produce the following effects:
- Anti-anxiety
- Stress relief
- Anticonvulsant
- Antidepressant
- Muscle relaxant
Asha strain high in Linalool: Commando, Sundae Driver
Myrcene
Myrcene is responsible for the earthy, spicy balsamic, and clove aromas. Myrcene can be found in hops, mango, lemongrass, and basil.
 Myrcene is found to produce the following effects:
Myrcene is found to produce the following effects:
- Antiseptic
- Analgesic
- Antimicrobial
- Antioxidant
- Anti-carcinogen
- Muscle relaxant
Asha strain high in Myrcene: LasoNo3, Super Glue, Super Sour Diesel, MedUsa
Pinene
The most common terpene, pinene, comes in two different varieties — alpha and beta. Alpha-pinene secretes aromas of pine needles or rosemary, while beta-pinene produces scents of hops, dill, parsley, or basil. Pinene is also found in turpentine, conifer trees, and orange peels.
 Pinene is found to produce the following effects:
Pinene is found to produce the following effects:
- Bronchodilator
- Anti-inflammatory
- Topical antiseptic
- Promotes alertness
- Analgesic
Asha strain high in Pinene: MedUsa
B-Caryophyllene
B-Caryophyllene has a woody, spicy scent. It’s found in basil, cloves, black pepper and cinnamon.
 B-Caryophyllene is found to produce the following effects
B-Caryophyllene is found to produce the following effects
- Reduces Inflammation
- Pain Relief
- Sleep Aid
Asha strains high in B-Caryophyllene: Super Sour Diesel, Candy Land, Gelato, Super Glue, Sherbet Cookies
Humulene
Humulene gives us those outdoor earthy, woody, herbal notes. It can be found in hops, basil, sage and cloves.
 Humulene is found to produce the following effects:
Humulene is found to produce the following effects:
- Pain relief
- Appetite Suppressant
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anti-Tumor
Asha strains high in Humulene: Super Sour Diesel, Sherbet Cookies,
Terpinolene
Terpinolene is recognized for its woody smell combined with floral citrus notes. It can be found in a variety of different things such as lilac, sage, rosemary, nutmeg, cumin, apple conifer trees, and tea trees.
 Terpinolene is found to produce the following effects:
Terpinolene is found to produce the following effects:
- Sleep Aid
- Ease hypertension
- Anti-anxiety
- Antioxident
- Antifungal
- Ease Restless Leg Syndrome
Asha strains high in Terpinolene: Black Jack,
Sources
![]() All photos are from iStock Photos
All photos are from iStock Photos
Surterra.com
CrescoLabs.com
Curaleaf.com
MedicalNewsToday.com
Everything you need to know about cannabis
Healthline.com
A Quick Take on Cannabis and Its Effects
Cannabis 101: What’s the Deal with Terpenes?
Healer.com
TheCannabist.com
The cannabis lexicon: Terms to know, from A-Z
Leafly.com
What are cannabis terpenes and what do they do?